ESP8266 ARDUINO CON WIFI
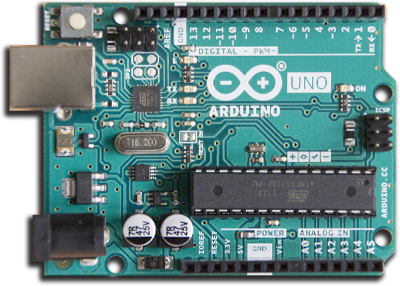
CARACTERÍSTICAS DEL ESP8266
Sketch
/*
Switch statement with serial input
Demonstrates the use of a switch statement. The switch statement allows you
to choose from among a set of discrete values of a variable. It's like a
series of if statements.
To see this sketch in action, open the Serial monitor and send any character.
The characters a, b, c, d, and e, will turn on LEDs. Any other character will
turn the LEDs off.
The circuit:
- five LEDs attached to digital pins 2 through 6 through 220 ohm resistors
created 1 Jul 2009
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/SwitchCase2
*/
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the LED pins:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 7; thisPin++) {
pinMode(thisPin, OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
// read the sensor:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int inByte = Serial.read();
// do something different depending on the character received.
// The switch statement expects single number values for each case; in this
// example, though, you're using single quotes to tell the controller to get
// the ASCII value for the character. For example 'a' = 97, 'b' = 98,
// and so forth:
switch (inByte) {
case 'a':
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
break;
case 'b':
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
break;
case 'c':
digitalWrite(4, HIGH);
break;
case 'd':
digitalWrite(5, HIGH);
break;
case 'e':
digitalWrite(6, HIGH);
break;
default:
// turn all the LEDs off:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 7; thisPin++) {
digitalWrite(thisPin, LOW);
}
}
}
}
map() [Matemáticas] Descripción Vuelve a mapear un número de un rango a otro. Es decir, un valor de fromLow se asignaría a toLow , un valor de fromHigh a toHigh , valores intermedios a valores intermedios, etc. No restringe los valores dentro del rango, porque los valores fuera de rango a veces son intencionales y útiles. La constrain()función puede usarse antes o después de esta función, si se desean límites a los rangos. Tenga en cuenta que los "límites inferiores" de cualquiera de los rangos pueden ser mayores o menores que los "límites superiores", por lo que la map()función se puede utilizar para invertir un rango de números, por ejemplo y = map(x, 1, 50, 50, 1); La función también maneja bien los números negativos, por lo que este ejemplo y = map(x, 1, 50, 50, -100); También es válido y funciona bien. La map()función usa matemática entera, por lo que no generará fracciones, cuando la matemática podría indicar que debería hacerlo. Los restos fraccionarios se truncan y no se redondean ni promedian. Sintaxis map(value, fromLow, fromHigh, toLow, toHigh) Parámetros value: el número a mapear. fromLow: el límite inferior del rango actual del valor. fromHigh: el límite superior del rango actual del valor. toLow: el límite inferior del rango objetivo del valor. toHigh: el límite superior del rango objetivo del valor. Devoluciones El valor mapeado.
Sketch
/*
Switch statement with serial input
Demonstrates the use of a switch statement. The switch statement allows you
to choose from among a set of discrete values of a variable. It's like a
series of if statements.
To see this sketch in action, open the Serial monitor and send any character.
The characters a, b, c, d, and e, will turn on LEDs. Any other character will
turn the LEDs off.
The circuit:
- five LEDs attached to digital pins 2 through 6 through 220 ohm resistors
created 1 Jul 2009
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/SwitchCase2
*/
void setup() {
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
// initialize the LED pins:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 7; thisPin++) {
pinMode(thisPin, OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
// read the sensor:
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int inByte = Serial.read();
// do something different depending on the character received.
// The switch statement expects single number values for each case; in this
// example, though, you're using single quotes to tell the controller to get
// the ASCII value for the character. For example 'a' = 97, 'b' = 98,
// and so forth:
switch (inByte) {
case 'a':
digitalWrite(2, HIGH);
break;
case 'b':
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
break;
case 'c':
digitalWrite(4, HIGH);
break;
case 'd':
digitalWrite(5, HIGH);
break;
case 'e':
digitalWrite(6, HIGH);
break;
default:
// turn all the LEDs off:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 7; thisPin++) {
digitalWrite(thisPin, LOW);
}
}
}
}
map() [Matemáticas] Descripción Vuelve a mapear un número de un rango a otro. Es decir, un valor de fromLow se asignaría a toLow , un valor de fromHigh a toHigh , valores intermedios a valores intermedios, etc. No restringe los valores dentro del rango, porque los valores fuera de rango a veces son intencionales y útiles. La constrain()función puede usarse antes o después de esta función, si se desean límites a los rangos. Tenga en cuenta que los "límites inferiores" de cualquiera de los rangos pueden ser mayores o menores que los "límites superiores", por lo que la map()función se puede utilizar para invertir un rango de números, por ejemplo y = map(x, 1, 50, 50, 1); La función también maneja bien los números negativos, por lo que este ejemplo y = map(x, 1, 50, 50, -100); También es válido y funciona bien. La map()función usa matemática entera, por lo que no generará fracciones, cuando la matemática podría indicar que debería hacerlo. Los restos fraccionarios se truncan y no se redondean ni promedian. Sintaxis map(value, fromLow, fromHigh, toLow, toHigh) Parámetros value: el número a mapear. fromLow: el límite inferior del rango actual del valor. fromHigh: el límite superior del rango actual del valor. toLow: el límite inferior del rango objetivo del valor. toHigh: el límite superior del rango objetivo del valor. Devoluciones El valor mapeado.